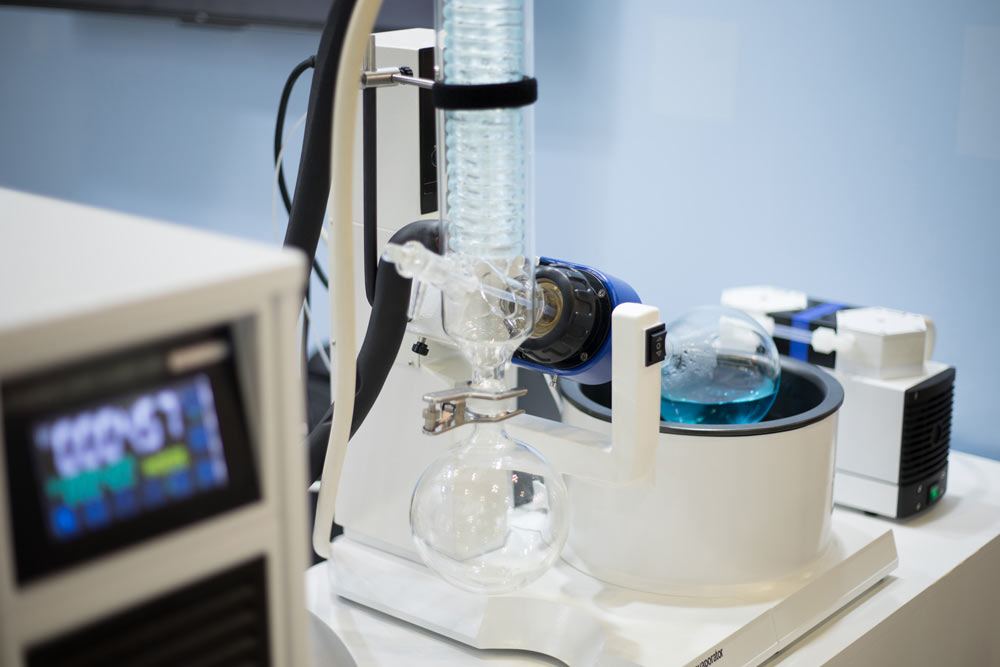
What Is a Rotary Evaporator?
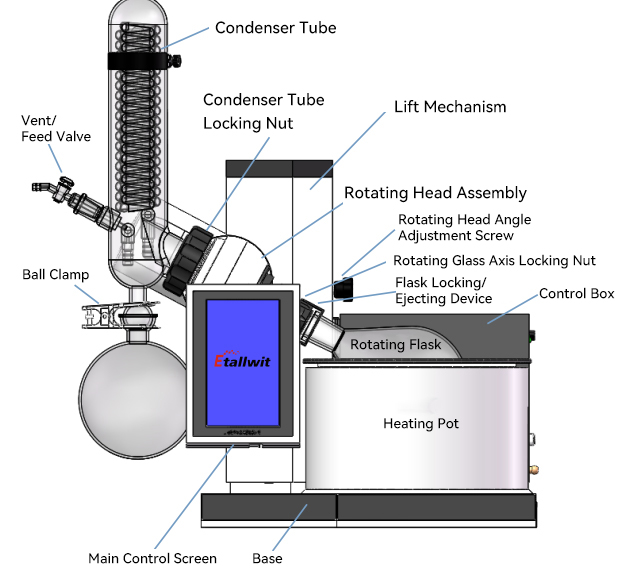
A rotary evaporator typically consists of components such as the rotating body, heating bath, condenser, and collection flask. Its principle involves increasing the surface area of the solution by rotating the evaporation flask under reduced pressure, thereby enhancing the evaporation rate to achieve rapid solvent separation. The rotary evaporator is easy to operate and highly efficient, making it one of the common devices in pharmaceutical and chemical laboratories.
If you're looking for a professional rotary evaporator for your lab, Etallwit’s solutions offer top-tier performance with reliable after-sales support.

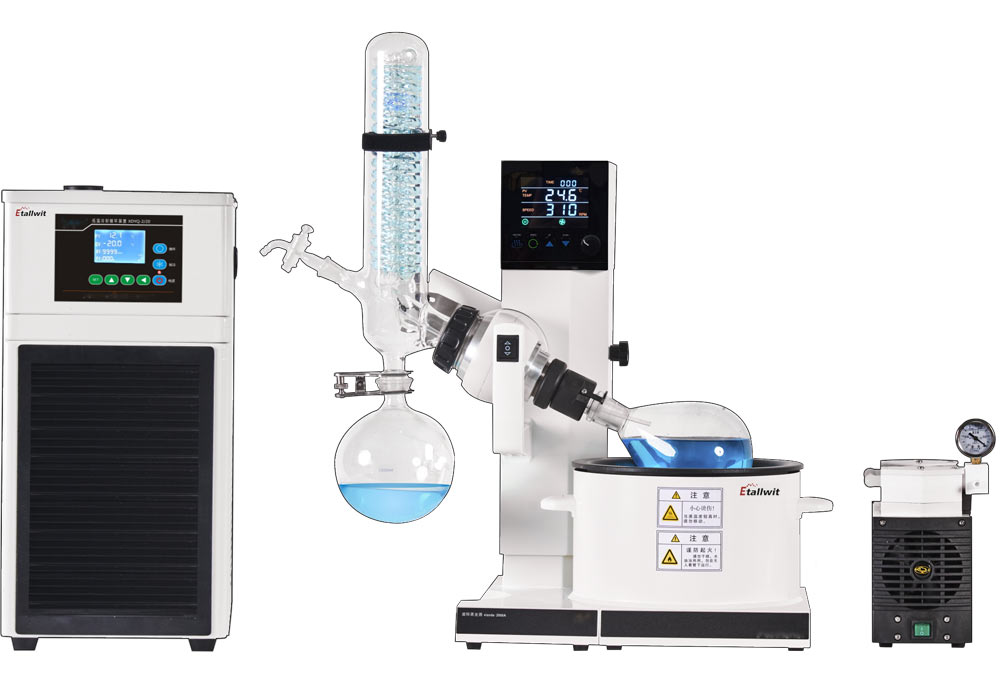
Core Components of a Rotary Evaporator
1. Rotating Evaporation Flask
The rotating evaporation flask is the container for the solution, typically made of high-temperature-resistant glass material with good chemical corrosion resistance. The capacity of the rotating evaporation flask can be selected based on experimental needs, with common laboratory capacities ranging from 50 mL to 5 L. Pilot-scale capacities range from 5 L to 50 L.
2. Heating Bath
The heating bath provides the heat source and usually features a temperature control system that can precisely regulate the temperature of the bath liquid. The heating bath can be a water bath or an oil bath, ensuring even heating and preventing overheating that could damage the solution. The common temperature range for a heating bath is from room temperature to 180°C.
3. Condenser
The condenser is an important component of the rotary evaporator, used to cool the solvent vapor that evaporates, causing it to condense into liquid. The condenser typically has a 2-3 layer structure, with the inner layer circulating cooling water or ice water and the outer layer receiving the vapor. The condensed solvent liquid then flows into the collection flask.
4. Collection Flask
The collection flask is used to receive the condensed solvent liquid. It is generally installed below the condenser and connected by a tube. The collected solvent can be further processed or recycled as needed.
5. Vacuum System
The vacuum system, usually consisting of a vacuum pump and a pressure regulation device, provides a low-pressure environment during the rotary evaporation process. This reduces the boiling point of the solvent, facilitating rapid evaporation. By adjusting the vacuum system, operators can control the temperature and rate of evaporation.
6. Rotary Motor and Support Stand
The rotary motor drives the rotation of the evaporation flask at a certain speed. The rotation speed typically ranges from 5 to 310 rpm and can be adjusted according to the characteristics of the solution and the desired evaporation rate. The support stand and motor mounting device stabilize the position of the rotating flask to ensure smooth operation.
Step-by-Step Operation Guide
1. Powering Up and Setting Up the Instrument
Connect Power and Water Sources
Ensure that the power supply and water source (for the condenser cooling) of the rotary evaporator are properly connected. The flow rate of the cooling water should be appropriate to ensure effective condensation, high recovery efficiency, and protection of the vacuum pump.
Check the Vacuum System
Turn on the vacuum pump and check whether the system is functioning properly. Ensure that the vacuum pump has sufficient suction to reduce the system pressure. Adjust the vacuum controller or pressure regulator to the appropriate working pressure.
Set the Heating Bath Temperature
Under reduced pressure, set the temperature of the heating bath according to the boiling point of the experimental material. Ensure that the temperature is uniform and avoid overheating of the solution. In routine operations, the heating bath temperature is typically set between 40°C and 80°C.
2. Sample Preparation and Loading
Prepare the Solution
According to the experimental requirements, prepare the solution and add it to the rotating evaporation flask (round-bottom flask). The volume of the solution should not exceed two-thirds of the maximum capacity of the rotating evaporation flask to prevent overflow.
Ensure Equipment Cleanliness
Ensure that the rotating evaporation flask, condenser, collection flask, and other components are clean and free of impurities to avoid sample contamination or interference with the evaporation process.
3. Initiating the Evaporation Process
Start the Rotary Motor
Turn on the rotary motor to start rotating the evaporation flask. Adjust the rotation speed according to the characteristics of the solution. Excessive rotation speed may cause the solution to splash out, while too low a speed may reduce evaporation efficiency.
Begin Heating and Vacuum Drawing
Set the appropriate vacuum pressure and start heating the solution in the heating bath. Through heating and vacuum action, the solvent will evaporate at a lower temperature. Adjust the vacuum level and heating temperature according to the volatility and boiling point of the solvent.
Monitor the Evaporation Process
Observe the evaporation of the solvent and check whether the condenser is working properly to ensure that the vapor condenses smoothly and flows into the collection flask.
4. Completion of Evaporation and Collection
End of Evaporation
When the solvent has been largely evaporated and the amount of solvent in the collection flask has significantly decreased, stop the evaporation process. Turn off the heating bath and vacuum pump (and release the vacuum inside the rotary evaporator), and stop the rotary motor.
Remove the Sample
After stopping the operation, remove the rotating evaporation flask and collection flask. For samples that need further concentration, increase the rotation speed or heating temperature to achieve the desired concentration.
5. Cleaning and Shutting Down the Instrument
Clean the Instrument
Clean all components promptly after use, especially the rotating evaporation flask and collection flask, to prevent residual solvents from contaminating or corroding the instrument.
Shut Down the Instrument
Release the pressure, turn off the main unit, vacuum pump, cooling water, and heating bath. Ensure that the instrument is completely shut down and check whether the equipment is in a standby state.
Best Practices & Safety Tips
1. Solvent Selection
When using a rotary evaporator, selecting an appropriate solvent is crucial. It is important to understand the solvent's boiling point, volatility, and whether it is flammable or explosive. Avoid using solvents with high boiling points or extremely high volatility.
2. Temperature and Vacuum Control
Excessively high temperatures may cause sample degradation. Therefore, the temperature of the heating bath should be set appropriately based on the properties of the solvent and the sample. The vacuum level should also be controlled properly to avoid too rapid or incomplete evaporation.
3. Safety Operations
When using a rotary evaporator, wear protective goggles and gloves, especially when handling volatile or toxic solvents. Ensure that the laboratory is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of harmful gases.
4. Instrument Maintenance
Regularly inspect all components of the rotary evaporator, especially the vacuum pump, condenser, and rotary motor, to ensure smooth operation of the equipment. Clean and maintain the instrument as necessary to extend its service life.

Why Choose Etallwit Rotary Evaporators?
ü High-speed & precision motor control
ü Corrosion-resistant materials
ü Flexible flask capacities from 1L to 20 L
ü Available with vacuum pumps & chillers as full sets
ü CE-certified safety mechanisms
Whether for R&D, pharma synthesis, or quality control, Etallwit delivers robust rotary evaporator systems tailored to your application.
Get Started with Etallwit
Etallwit Rotary Evaporator, meeting your diverse needs. Whether in pharmaceutical research and development, chemical experiments, or other fields, our rotary evaporator can provide you with efficient and safe experimental solutions. Welcome to inquire for more product information to help your scientific research work go more smoothly!
Ready to upgrade your lab?
Contact Etallwit’s expert team to request a quote or consultation.



