A laboratory centrifuge is a vital device for separation technologies, widely used in biomedicine, chemical analysis, and more. It uses centrifugal force to separate particles or liquids of different densities. In this article, we'll explore how a centrifuge works and break down its core components, helping you understand this "separation wizard" in the lab.
Working Principle of the Centrifuge & Centrifugal Force Calculation
How does a centrifuge work?
The principle behind a centrifuge is simple: during high-speed rotation, centrifugal force causes suspended solids in a liquid to settle. Larger particles move outward toward the perimeter of the rotor, while smaller particles settle closer to the center.
Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is the force that pushes an object outward when it is rotating, similar to how water is thrown out of clothes in a washing machine during the spin cycle.
Centrifugal Force Calculation
The magnitude of centrifugal force is determined by the rotor speed (rpm) and the radius (R) of the rotor. The formula for calculating centrifugal force (RCF) is:
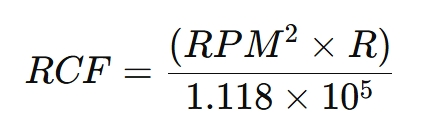
Key points:
· RCF = Relative centrifugal force
· RPM = Rotations per minute
· R = Rotor radius
At the same rpm, a larger rotor produces a greater centrifugal force.
Core Components of a Centrifuge
A centrifuge’s performance depends on several key components, including the motor, rotor, adapter, control system, and cooling system. The quality and functionality of each component directly affect separation efficiency and operational safety.
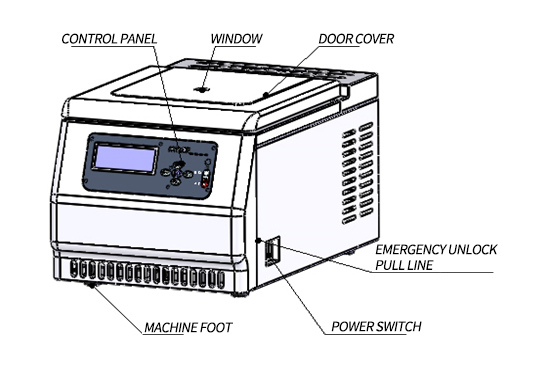
For example, the Etallwit H1850R High-Speed Refrigerated Centrifuge consists of the main body, rotor, and accessories. The main unit includes the centrifuge chamber, drive system, cooling system, and control panel.
Key Components:
1. Motor: The Core Power Source
The motor is the heart of the centrifuge, providing the rotation power. A high-speed motor is essential for optimal separation efficiency. Domestic centrifuges often rely on imported motors, and technology advancements in this area can help improve the competitiveness of domestic products.
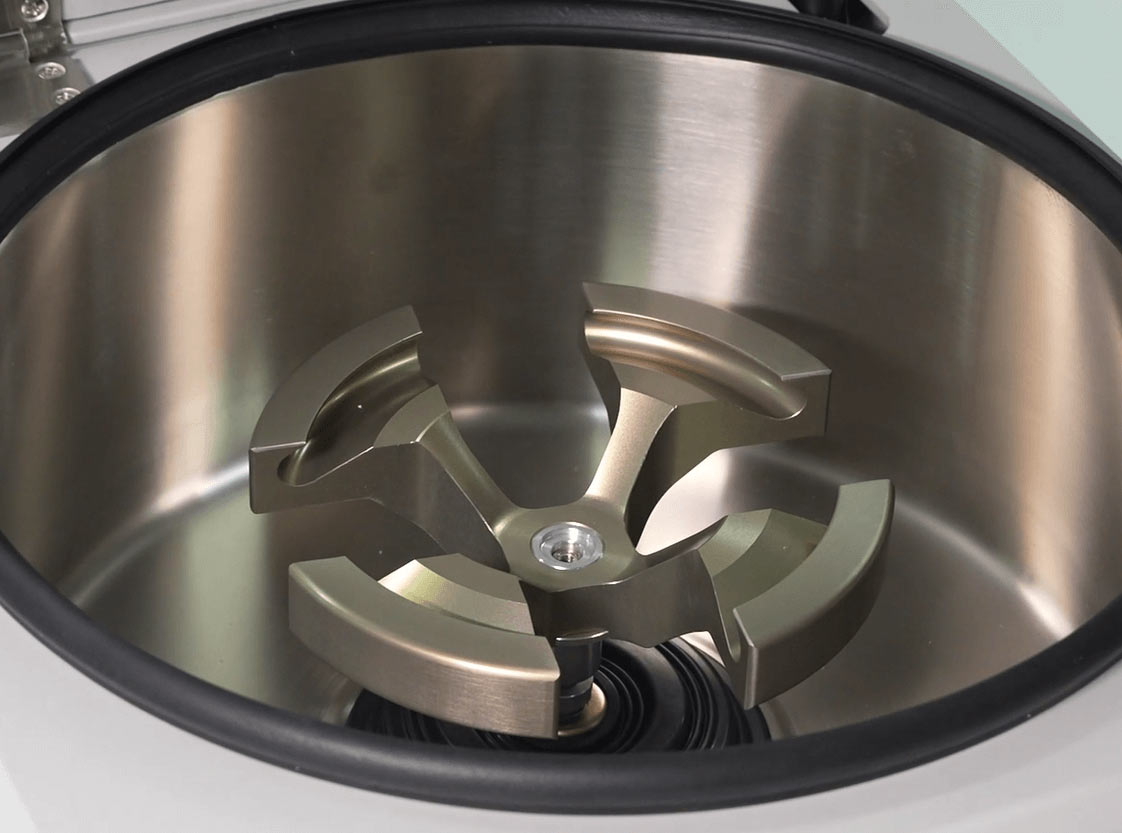
2. Rotor: The Key to Separation
The rotor holds the samples and is directly involved in the separation process. The rotor type and design greatly impact centrifugation efficiency.
· Angle Rotors: Hold test tubes at a 14°-40° angle, suitable for differential centrifugation and commonly used for blood separation and other rapid separations.
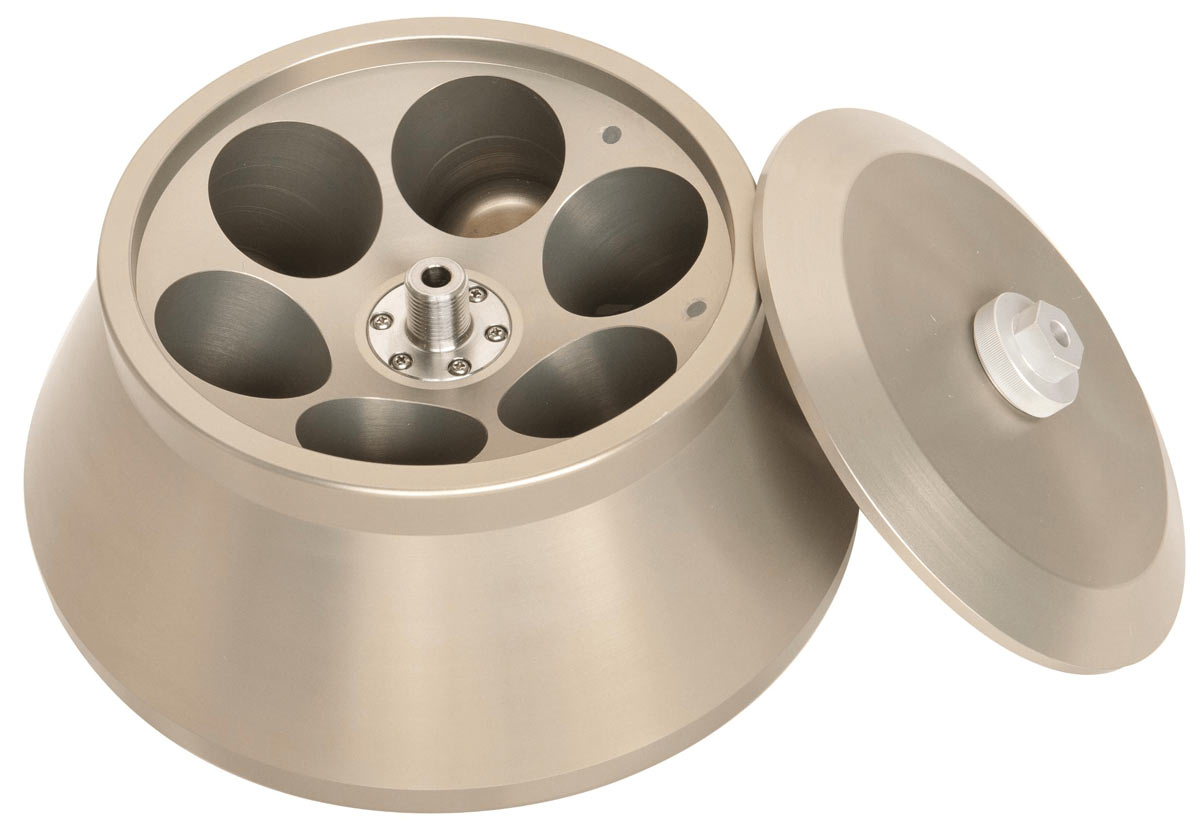

· Horizontal Rotors: Hold test tubes horizontally, ideal for fine layering and density gradient centrifugation, such as DNA separations.

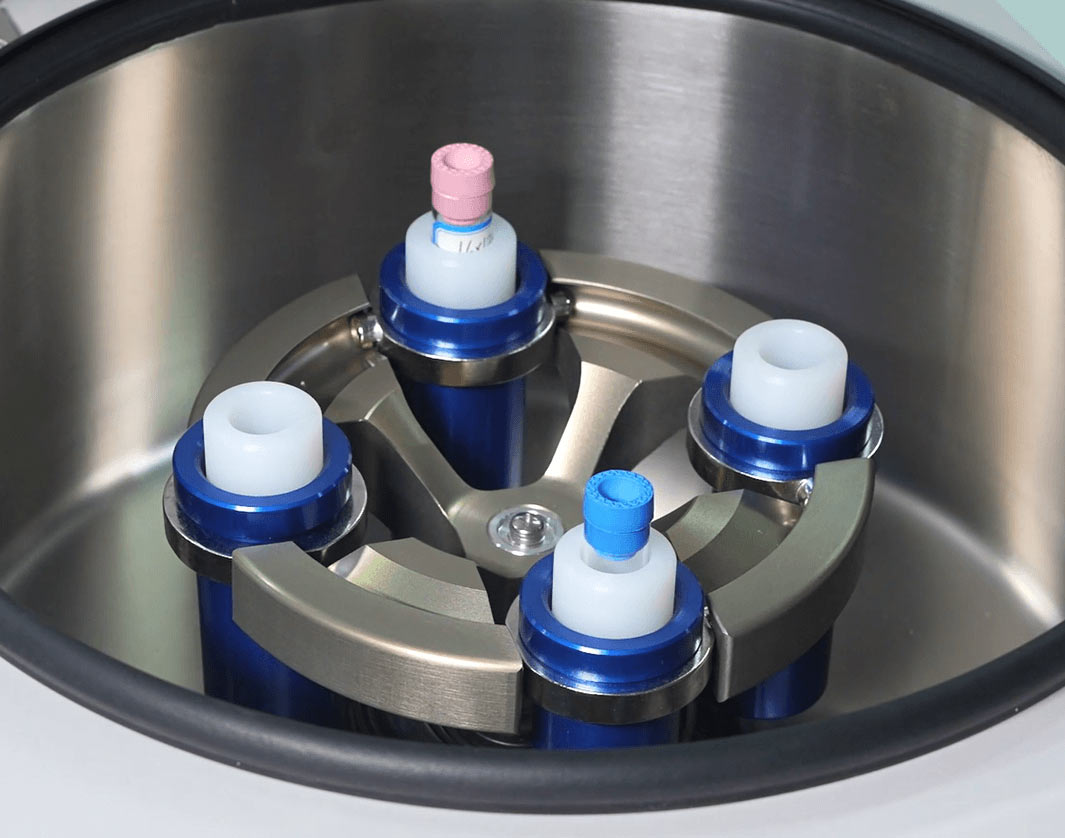
3. Adapter: Ensuring Sample Compatibility
The adapter is an essential part of the centrifuge, allowing various types of containers (e.g., test tubes, blood bags, microplates) to fit the rotor.

4. Control System: Precise Parameter Management
The control system adjusts key parameters like speed, time, and temperature. High-end centrifuges often feature programmable settings, data recording, and user access control to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories.


5. Cooling System: Protecting Temperature-Sensitive Samples
The cooling system is crucial in refrigerated centrifuges, preventing samples from denaturing due to heat buildup, particularly when dealing with proteins or cell cultures.
6. Safety Locks and Covers
The centrifuge only operates when the lid is securely closed and locked. This safety feature prevents accidental sample leaks or injuries from high-speed operation.
7. Software System: Intelligent Operation
Advanced centrifuges come with software systems that manage key parameters, allow for pulse centrifugation, provide error warnings, and log data. They help simplify operations and improve laboratory workflow.
Centrifuge Consumables
Consumables include various centrifuge tubes (1.5ml, 2ml, 5ml, 15ml, 50ml, etc.), test tubes, blood bags, and microplates. These materials must withstand high pressures, ensure tight seals, and resist corrosion, particularly during high-speed applications.
Market Trends
While the market for standard centrifuge consumables is highly competitive, high-end consumables are predominantly led by international brands like Eppendorf and Thermo Fisher. However, Etallwit Scientific continues to improve its domestic consumable offerings, with breakthroughs in pressure resistance, high sealing, and other critical properties.
Although seemingly simple, centrifuges integrate materials science, mechanical engineering, and biotechnology. Every component, from the motor to the centrifuge tubes, plays a crucial role in the success of an experiment. In the next article, we will explore the types of centrifuges and how to choose the best one for your laboratory.
Want to Learn More?
If you need help selecting the right centrifuge for your laboratory, feel free to contact Etallwit Scientific today. Our team of experts is here to assist you in finding the ideal centrifuge solution for your scientific research needs.
Contact us for expert advice and product recommendations!



